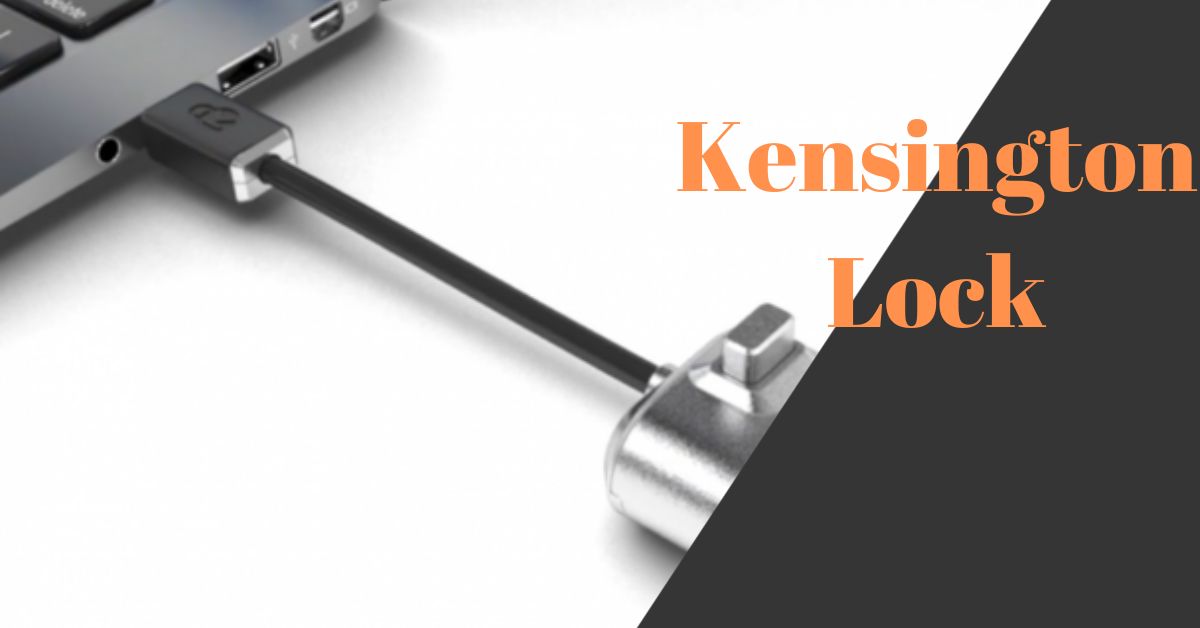
What is a Kensington lock? A Kensington lock secures mobile electronic devices against theft. It is a security cable with a lock. At one end, it is firmly connected to the device to be secured; at the other end, it is connected to a stationary object or a fixed mount.
In the cyber world where the security of our devices and data is paramount, innovative solutions have emerged to safeguard our valuable possessions. One such solution is the Kensington Lock, a simple yet effective tool designed to protect your laptops, computers, and other devices from theft.
In this article, we will delve into the world of Kensington Locks, exploring what they are, how they work, and why they are an essential addition to your security toolkit.
Contents
- What is a Kensington lock?
- Kensington lock Components
- How Does a Kensington Lock Work?
- Where are Kensington Locks Used?
- Benefits of Using a Kensington Lock
- Types of Kensington Locks
- How to Choose the Right Kensington Lock
- Installing and Using a Kensington Lock – Step-by-Step Guide
- Kensington Lock Alternatives
- Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the history of Kensington Locks?
- Are Kensington Locks effective?
- Can Kensington Locks be used with any device?
- Are there any security concerns with Kensington Locks?
- Can Kensington Locks be removed without the key?
- Are there wireless alternatives to Kensington Locks?
- Do Kensington Locks work with desktop computers?
- Can Kensington Locks damage the device?
- What are the best practices for using Kensington Locks?
- How much does a Kensington Lock cost?
What is a Kensington lock?
Kensington Locks from $15+ on Amazon
A Kensington Lock, often referred to simply as a “K-lock” or “Kensington Security Slot,” is a small, secure, and widely used anti-theft device designed to prevent theft of portable electronic devices, primarily laptops and desktop computers. It’s named after the company Kensington, which popularized this security solution.
The primary purpose of a Kensington Lock is to deter opportunistic theft and provide an extra layer of protection for your valuable equipment in various environments, including offices, libraries, public spaces, and even homes. It’s an invaluable tool for anyone who needs to leave their electronic devices unattended for any period.
Kensington lock Components
Kensington Locks consist of two main components: a lock head and a steel cable.
Lock Head
The lock head is a small, rectangular or circular mechanism that contains the locking mechanism. It typically has a slot or hole through which the locking cable is inserted. The lock head often comes with a key or combination lock system. Some modern Kensington Locks even offer digital options, such as electronic keypads or biometric authentication.
Steel Cable
The steel cable is a strong, flexible wire that attaches to the lock head at one end and has a loop or looped end at the other. In many cases, this looped end is designed to fit around an immovable object, like a desk leg or a specially designed anchoring point. The cable varies in length, allowing users to choose the appropriate size for their specific security needs.
When in use, the cable is looped around the chosen anchor point, and the lock head is inserted into the Kensington Security Slot, which is a small, elongated hole or slot found on most laptops, desktops, and other compatible devices. Once securely connected, the user can lock the device using a key, combination, or other locking mechanism.
In essence, a Kensington Lock provides a physical deterrent against theft by making it difficult for thieves to grab and run with your valuable equipment quickly. It offers a practical and relatively low-cost solution for enhancing the security of your devices in various settings.
How Does a Kensington Lock Work?
Kensington Locks are designed to provide a straightforward yet effective way to secure portable electronic devices.
Locking Mechanism
The core of a Kensington Lock is its locking mechanism, which can be one of several types:
- Keyed Lock: This is the traditional Kensington Lock, which uses a key to lock and unlock the device. The user inserts the key into the lock head, turns it to engage the locking mechanism, and then removes the key to secure the device.
- Combination Lock: Instead of a key, combination locks use a dial with numbers or letters to set a unique combination. To lock the device, the user rotates the dial to align the correct combination, and then they can secure the device. This eliminates the need for a physical key but requires remembering or recording the combination.
- Digital Lock: Modern Kensington Locks may feature digital locking mechanisms, such as electronic keypads or biometric readers (e.g., fingerprint or retina scanners). Users need to enter a PIN code or use their biometric data to lock and unlock the device. Digital locks offer added convenience and security, as they eliminate the risk of losing a physical key.
Attaching a Kensington Lock
The process of attaching a Kensington Lock to a device is relatively simple:
a. Locate the Kensington Security Slot: Most laptops, desktop computers, and other compatible devices come equipped with a Kensington Security Slot. This slot is typically found on the side or rear of the device and is identifiable by its elongated, rectangular or oval shape.
b. Insert the Lock Head: Insert the lock head of the Kensington Lock into the Kensington Security Slot on the device until it clicks into place. This securely anchors the lock head to the device.
c. Secure the Cable: Take the steel cable attached to the lock head and loop it around an immovable object. Common anchor points include desk legs, monitor stands, or specially designed anchor points in public spaces. Ensure the cable is taut, leaving no slack.
d. Engage the Locking Mechanism: Depending on the type of lock, use the key, combination dial, or digital input method to engage the locking mechanism. This prevents the lock head from being removed from the Kensington Security Slot.
e. Test the Lock: Give the cable a gentle tug to ensure it’s securely fastened to both the device and the anchor point. If properly attached, the device should remain securely in place.
Where are Kensington Locks Used?
Kensington Locks find applications in various settings where physical security of electronic devices is crucial:
- Laptop and Computer Security: The most common use of Kensington Locks is to secure laptops and desktop computers. Professionals, students, and individuals who need to leave their devices unattended in libraries, coffee shops, airports, and other public spaces often rely on Kensington Locks.
- Office and Business Environments: In office settings, Kensington Locks prevent unauthorized access to workstations and secure valuable computer equipment. IT departments may also use Kensington Locks to deter theft of servers and networking equipment.
- Educational Institutions: Educational institutions, such as schools and universities, deploy Kensington Locks to protect computer labs and classroom equipment, ensuring that valuable assets remain in place and available for use.
- Trade Shows and Conferences: Companies often use Kensington Locks to secure electronic devices, such as tablets and displays, at trade shows and conferences to prevent theft or tampering.
- Public Libraries and Internet Cafes: Public facilities with shared computer resources often provide Kensington Locks for patrons to secure devices while using them.
- Home Use: Some individuals even use Kensington Locks in their homes to protect personal computers and laptops from theft, especially in shared living spaces.
Benefits of Using a Kensington Lock
Using a Kensington Lock provides several valuable benefits, making it a practical choice for enhancing the security of your electronic devices:
Theft Deterrence
The primary benefit of a Kensington Lock is its ability to deter theft effectively. By physically securing your device to an immovable object, it becomes much more challenging for opportunistic thieves to grab and run with your equipment. This deterrence factor is especially crucial in public spaces and shared environments.
Portability and Convenience
Kensington Locks are designed to be portable and easy to use. They can be quickly attached to and detached from your device, allowing you to maintain the mobility and flexibility of your laptop or other equipment while ensuring its security. This convenience is especially valuable for professionals who frequently work on the go.
Types of Kensington Locks
Kensington Locks come in various types to accommodate different security needs and preferences.
Standard Kensington Locks
Standard Kensington Locks are the traditional version of these security devices. They consist of a lock head and a steel cable. The lock head is secured using a key. Users insert the key, turn it to lock the device, and remove it to unlock. Standard Kensington Locks are reliable and straightforward, providing a cost-effective solution for many users.
Combination Kensington Locks
Combination Kensington Locks eliminate the need for a physical key. Instead, they use a combination dial or digital keypad to set and input a unique code. Users rotate the dial or enter the correct code to lock and unlock the device. Combination locks offer the advantage of not needing to carry or keep track of a physical key, reducing the risk of key loss.
Keyed Kensington Locks
Keyed Kensington Locks are similar to standard Kensington Locks but come with a unique key for each lock. This means that each lock can only be opened with its corresponding key. Keyed locks provide an added layer of security, as the key is not interchangeable between locks. They are suitable for situations where multiple devices need individual security.
Digital Kensington Locks
Some advanced Kensington Locks feature digital locking mechanisms like electronic keypads or biometric readers. Users enter a PIN code or use biometric authentication (fingerprint or retina scan) to lock and unlock the device. Digital locks offer the highest level of security and user convenience, eliminating the risk of losing keys and providing quick access to the secured device.
The choice of Kensington Lock type depends on your specific security requirements and personal preferences. Standard locks are reliable and cost-effective, while combination and digital locks offer added convenience. Keyed locks are ideal for situations where multiple devices require individual security measures.
How to Choose the Right Kensington Lock
Choosing the right Kensington Lock is essential to ensure it meets your specific security needs and device requirements.
Kensington Security Slot
Ensure that your device has a Kensington Security Slot. Most laptops and desktops include this slot, but some ultra-thin or custom-built devices may not. Check your device’s manual or consult the manufacturer to confirm compatibility.
Slot Location
Pay attention to the location of the Kensington Security Slot on your device. Some devices have the slot on the side, while others may have it on the rear or another location. Make sure the lock’s cable length and orientation fit the slot’s location.
Lock Strength
- Cable Thickness: Consider the thickness and strength of the cable. Thicker cables offer more resistance to tampering and cutting. If you plan to secure high-value equipment, opt for a thicker cable.
- Material Quality: Look for locks made from durable materials like steel. A robust lock is more resistant to physical attacks.
- Locking Mechanism: Choose a locking mechanism that aligns with your security preferences. Standard locks with keys are reliable but require careful key management. Combination and digital locks offer added convenience but may have a learning curve for setup.
Additional Features
- Key Management: If you choose a lock with keys, consider the number of keys provided and whether you can obtain replacements if needed. Some locks come with a master key for added convenience.
- Combination: For combination locks, decide whether you prefer a preset combination or the ability to set your code. Ensure the combination is easy for you to remember but not easily guessable.
- Digital Features: If you opt for a digital lock, check if it has additional security features, such as anti-tamper alarms or remote locking capabilities.
- Cable Length: Choose a cable length that allows you to secure your device to an immovable object comfortably. Longer cables provide more flexibility but may be bulkier to carry.
- Warranty: Check if the lock comes with a warranty. A warranty can provide peace of mind in case of lock malfunctions or defects.
Installing and Using a Kensington Lock – Step-by-Step Guide
Locate the Kensington Security Slot
Find the Kensington Security Slot on your device. It’s usually a small, elongated hole or slot.
Insert the Lock Head
Insert the lock head of the Kensington Lock into the Kensington Security Slot on your device until it clicks into place.
Secure the Cable
Loop the steel cable of the lock around an immovable object, such as a desk leg, monitor stand, or another anchor point.
Engage the Locking Mechanism
Use the locking mechanism according to the lock type you have (key, combination, or digital). Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for locking and unlocking your device.
Test the Lock
Give the cable a gentle tug to ensure it’s securely fastened to both the device and the anchor point. The device should remain securely in place.
Record Key or Combination (if applicable)
If you’re using a keyed or combination lock, record the key or combination in a safe place. Consider storing it securely but separately from the locked device.
Regularly Inspect and Maintain
Periodically inspect the lock and cable for any signs of wear or damage. Lubricate the lock mechanism if necessary, and replace worn cables or locks promptly.
Kensington Lock Alternatives
Security Cable Locks
Security cable locks are similar in function to Kensington Locks but often come with some differences in design and locking mechanisms.
- Cable Design: These locks typically consist of a steel cable that is looped around an anchor point and then secured to the device using a lock or combination mechanism, similar to Kensington Locks.
- Compatibility: Many security cable locks are designed to be compatible with a wider range of devices beyond laptops and desktops. This includes monitors, projectors, and other valuable equipment.
- Variety of Lock Types: Security cable locks may offer various locking mechanisms, including keyed locks, combination locks, and digital locks, similar to Kensington Locks.
Advantages:
- Device Versatility: Security cable locks are versatile and can be used with a broader range of equipment beyond laptops.
- Choice of Lock Type: Users can choose the lock type that best suits their preferences and security requirements.
Laptop Security Plates
Laptop security plates are physical metal plates that attach directly to your laptop’s chassis and are designed to secure it to a fixed anchor point.
- Attachment Method: These plates are affixed to the laptop’s exterior using strong adhesive or screws. They provide a permanent or semi-permanent attachment point for a cable lock.
- Slim Profile: Laptop security plates are designed to have a slim profile, so they don’t add much bulk to your laptop.
- Anti-Tamper Features: Some security plates come with features that make them tamper-resistant, such as sensors that trigger an alarm if someone attempts to remove the plate.
Advantages:
- Minimal Bulk: Laptop security plates don’t add much bulk or weight to your laptop, making them a discreet security option.
- Permanent Attachment: Once installed, these plates remain on your laptop, providing a constant anchor point for a cable lock.
Considerations
- Permanent Attachment: The permanent or semi-permanent attachment of security plates means that you won’t be able to easily remove them if you want to change laptops or devices.
- Compatibility: Ensure that the security plate you choose is compatible with your specific laptop model.
Choosing Between Alternatives
The choice between Kensington Locks, Security Cable Locks, and Laptop Security Plates depends on your specific security needs, the devices you want to protect, and your preference for portability and ease of use.
Kensington Locks remain a popular choice for their ease of use and compatibility with many devices, while security cable locks and laptop security plates offer alternative solutions with their own advantages and considerations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the history of Kensington Locks?
Kensington Locks were introduced by the company Kensington Computer Products Group in the early 1990s. The locks were designed to address the need for a simple and effective way to secure laptops and other portable devices. They quickly gained popularity and have since become a widely recognized and used security solution.
Are Kensington Locks effective?
Kensington Locks are effective at deterring opportunistic theft and providing an additional layer of security for laptops and other portable devices. While they may not be completely theft-proof, they serve as a valuable deterrent in various environments.
Can Kensington Locks be used with any device?
Kensington Locks are designed to work with devices that have a Kensington Security Slot. Most laptops, desktops, monitors, and some projectors have these slots. However, not all devices have this feature, so it’s essential to check your device’s compatibility.
Are there any security concerns with Kensington Locks?
Kensington Locks are effective against casual theft but may not stop determined thieves with the right tools and knowledge. There have been instances where thieves have removed Kensington Locks using specialized equipment. Users should be aware of this limitation and consider additional security measures.
Can Kensington Locks be removed without the key?
While Kensington Locks are designed to be tamper-resistant, determined thieves with the right tools and skills can potentially remove them without the key. However, this is relatively rare in casual theft scenarios.
Are there wireless alternatives to Kensington Locks?
Wireless alternatives to Kensington Locks typically involve tracking and remote disabling of devices. Some software solutions allow you to track and remotely lock or wipe your device in case of theft, but they don’t physically secure the device like Kensington Locks do.
Do Kensington Locks work with desktop computers?
Yes, Kensington Locks can be used with desktop computers that have a Kensington Security Slot. Many desktops, particularly all-in-one computers, have this slot, allowing users to secure the entire desktop unit.
Can Kensington Locks damage the device?
When used correctly, Kensington Locks should not damage the device. The lock is designed to fit snugly into the Kensington Security Slot without causing harm. However, users should be cautious not to use excessive force when inserting or removing the lock to avoid any potential damage.
What are the best practices for using Kensington Locks?
Best practices for using Kensington Locks include selecting the right lock type, securing the cable to an immovable object, regularly inspecting the lock and cable for wear, and recording key or combination details (if applicable). For detailed guidance, refer to the earlier section on “Installing and Using a Kensington Lock – Step-by-Step Guide.”
How much does a Kensington Lock cost?
The cost of Kensington Locks varies depending on the type of lock (standard, combination, digital, etc.) and the brand. Standard Kensington Locks can range from $20 to $50, while more advanced or digital locks may cost upwards of $100 or more. Prices may also vary based on cable thickness and additional features.
Kensington Locks offer a practical and effective way to enhance the security of your valuable devices. Whether you’re a student, a business professional, or anyone concerned about protecting your technology investments, understanding Kensington Locks and their benefits can help you safeguard your devices and data from potential threats.

Information Security Asia is the go-to website for the latest cybersecurity and tech news in various sectors. Our expert writers provide insights and analysis that you can trust, so you can stay ahead of the curve and protect your business. Whether you are a small business, an enterprise or even a government agency, we have the latest updates and advice for all aspects of cybersecurity.